GPS and GNSS antennas for precision location applications
What are GNSS/GPS antennas?
GNSS communications is the most widely used wireless technology for locational applications. It consists of signals and transmissions between the various satellite constellations (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou) and individual devices. From the trilateration of these transmissions, devices are able to pinpoint their exact location on a global scale.
When it comes to GNSS antenna integration, there are integral factors that determine the overall design of a device. GNSS/GPS reception consumes more power when compared to other wireless communications as the satellite signals are significantly weaker. They also need sufficient bandwidth and protection from interference to perform effectively. All of these factors need to be considered when choosing the specific GNSS/GPS antenna solution.
Types of GNSS and GPS antennas
Ceramic patch antennas
Ceramic patch antennas are embedded and printed directly onto a device’s PCB. It consists of a rectangular or circular patch of ceramic material that can radiate, acting as a gateway for RF signals; the larger the patch, the wider the access to different frequency bands. The patch itself also acts as the ground plane for the antenna. Moreover, GPS stacked patch antennas have an even greater bandwidth by utilising a greater surface area without taking up valuable PCB space.
In terms of GNSS communication, patch GNSS antennas are commonplace for a range of devices. They support the varying frequency bands of the different constellations (1176 MHz – 1575.42 MHz), exhibit impressive performance and are relatively inexpensive to mass produce. That said, there are various design limitations that can make ceramic patch antenna integration a challenge. For example, they need to be pointed directly upwards for effective performance, or suffer from a prolonged TTFF (time-to-first-fix).
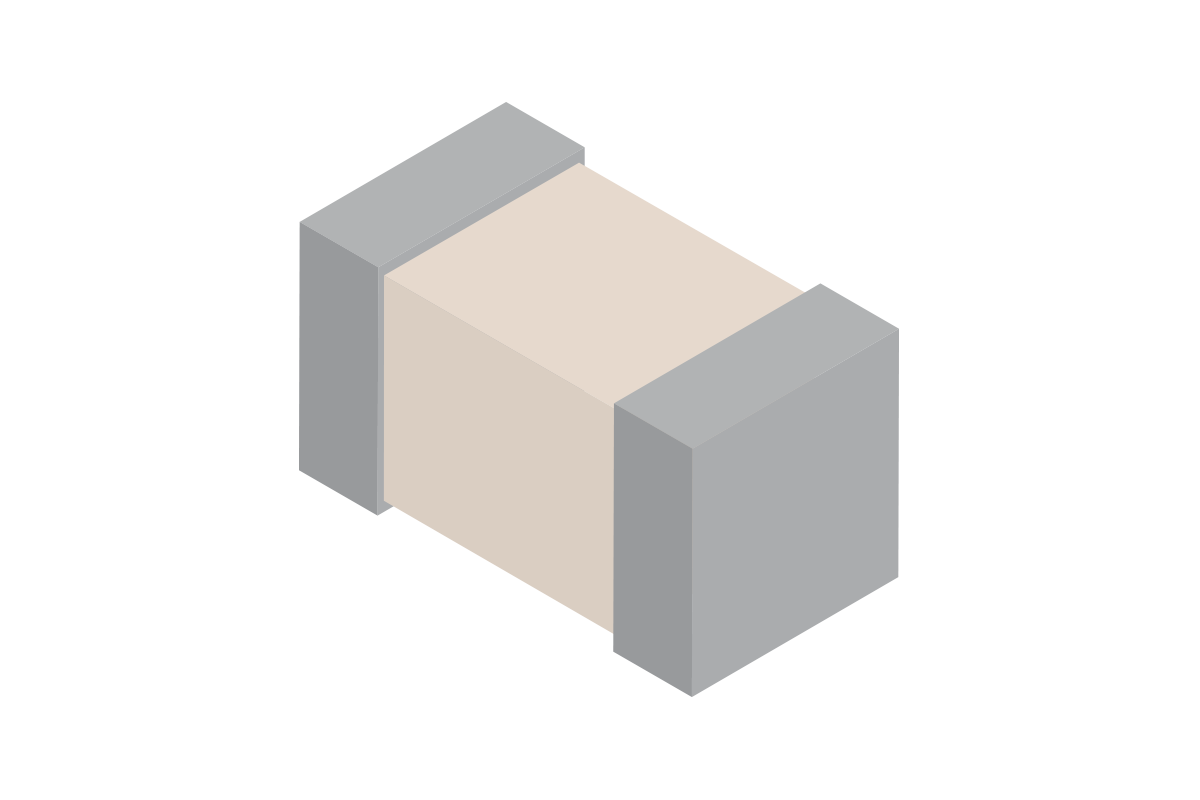
PCB trace antennas
GNSS/GPS module
GNSS/GPS antenna applications
Logistics
The efficient transportation and delivery of goods and products are optimised by effective route planning and accurate location information. This is especially true for cold chain, where the location and time spent outside of optimal temperatures are absolutely vital. GNSS antennas provide businesses with accurate and reliable information to improve processes and prevent goods from perishing.
Security
Depending on the specific asset, having tracking capabilities via GNSS communication provides businesses with a holistic view of where their assets are in real time. Moreover, it also provides an opportunity for reclamation if they do end up going missing. The battery efficiency and compact size of GNSS modules and antennas gives businesses a reliable tracking solution that can maintain communication for long periods.
Select the perfect GNSS antenna solution for your device
Each GNSS antenna technology presents a range of features that are applicable for different asset tracking devices. That said, GNSS modules proves to be the best all-rounder, having ease of integration, high efficiency and reliable connectivity. At Antenova, we offer a range of GNSS modules and antenna solutions that exhibit impressive features, such as our recently launched M20047-1 that works in unison with cellular connectivity.
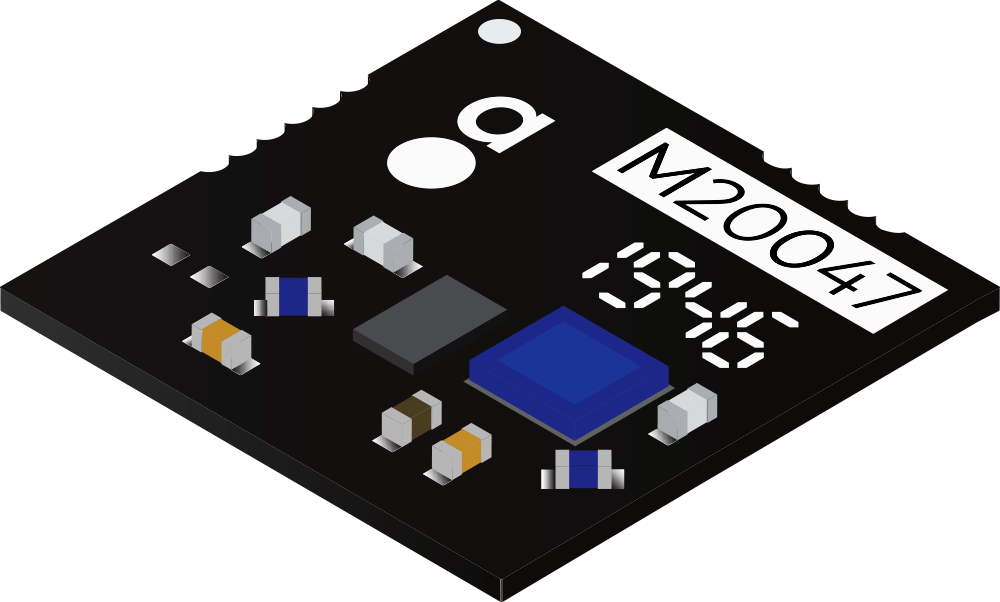
Introducing M20047-1
Made of FR4, M20047-1 offers a predictable, robust solution for devices used in fluctuating temperatures, conditions and environments. In changing temperatures, ceramic and FR4 thermally expands and contracts at different rates, straining solder joints and reducing the useful life of the device. FR4-on-FR4 makes this thermal expansion and contraction more predictable.
Plus, M20047-1 have matching circuits on-board, eliminating the need to spend any time creating a matching network. With this, Active GNSS is less susceptible to detuning, even when embedded within composite plastic housings. Additionally, its LNA and SAW are reversed for optimum performance in applications with cellular modems. To find out more about how M20047-1 can benefit your device design, contact a member of our team today.