GNSS & GPS Modules: The Ultimate Guide

All-in-one digital receivers
GNSS and GPS modules are all-in-one digital receivers with a down-converter that enables access to location and timing signals from satellites. They receive transmissions from satellites and use distance calculations to provide real-time locational data.
What are GNSS and GPS modules?
GNSS and GPS modules are either transmitters that have antennas or receivers that do not, and they are both all-in-one modules that can be integrated into wireless devices with minimal effort. GNSS and GPS modules that come with an antenna use a LNA (low noise amplifier) and a SAW (surface acoustic wave) filter to help boost performance.
GNSS and GPS modules contain all the components, RF circuitry and antennas needed to connect to GPS and GNSS satellites. Modules receive timestamp data to ascertain the location of a device–all in an easy-to-integrate, compact format.
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) describes the various satellite constellations used around the world such as GPS, GLONASS and Galileo. GNSS receivers use signals from multiple satellites in any of these constellations and use trilateration for pinpoint accuracy. GPS (Global Positioning System) refers to a specific type of GNSS which was developed in the 1990s as the world’s first satellite constellation for navigation. GPS receivers use satellites that are from that specific constellation rather than others like with GNSS.
GNSS and GPS modules are used in navigation, positioning and timing applications such as personal navigation and asset tracking due to their precise locational properties. Through transmissions received from multiple satellites GNSS/GPS offers reliable reception in locations all over the world. Understanding how GNSS/GPS modules are integrated and perform is paramount to choosing the right module for specific applications.

How do GNSS and GPS modules operate?
GNSS and GPS modules acquire signals from multiple satellites (at least four) to provide a position fix. Satellite signals are significantly weaker when compared to other wireless technologies like cellular and Wi-Fi, so performance is critical for GNSS/GPS modules in order to ensure accuracy.
The most significant measurement of GNSS performance for modules is TTFF (time-to-first-fix). TTFF is the amount of time it takes for the module to obtain a position fix after powering up from receiving a satellite signal. TTFF is usually separated into three scenarios: hot, warm and cold. Hot is typically when the TTFF is no higher than 1 second with rapid acquisition of satellite signals. Warm has a TTFF of 25 seconds or shorter, whereas cold is typically 35 seconds or lower.
The performance measurement for GNSS/GPS modules is important as a lower TTFF is needed to maintain manageable levels of power consumption, which is a common obstacle in satellite communications.

How can you increase battery life using GNSS?
GNSS/GPS reception consumes more power when compared to other wireless communications as the satellite signals are significantly weaker. The radio channel between the satellite and module is fairly slow at a data rate of 50 bits per second. The longer the TTFF measurement, the more power is consumed; a strong signal can take a few seconds whereas a weak signal can take over half a minute.
The antennas within GNSS/GPS modules can be tuned by means of a tuning circuit (Pi Network) to increase the antenna’s ability to receive the GNSS/GPS signal. As the satellite signal is so weak, the module allows the antenna to be tuned to reduce TTFF without being affected by other device components. Antenova’s GNSS/GPS modules are optimised to maximise performance and provide a stable connection without negatively impacting power consumption.
How do you integrate GNSS and GPS modules?
Because of the sensitivity involved with GNSS/GPS communications, modules require careful integration. The often used ceramic patch GNSS/GPS antennas need to be placed in the centre of the PCB, which is where the most important processing chips usually are.

Which GPS and GNSS modules are right for your device?
GNSS and GPS modules are available in a variety of configurations, each offering designers a different set of features and advantages. Every application will have an optimum solution. Here, we explain just how to review the range of modules available on the market and select the most appropriate module for your application.
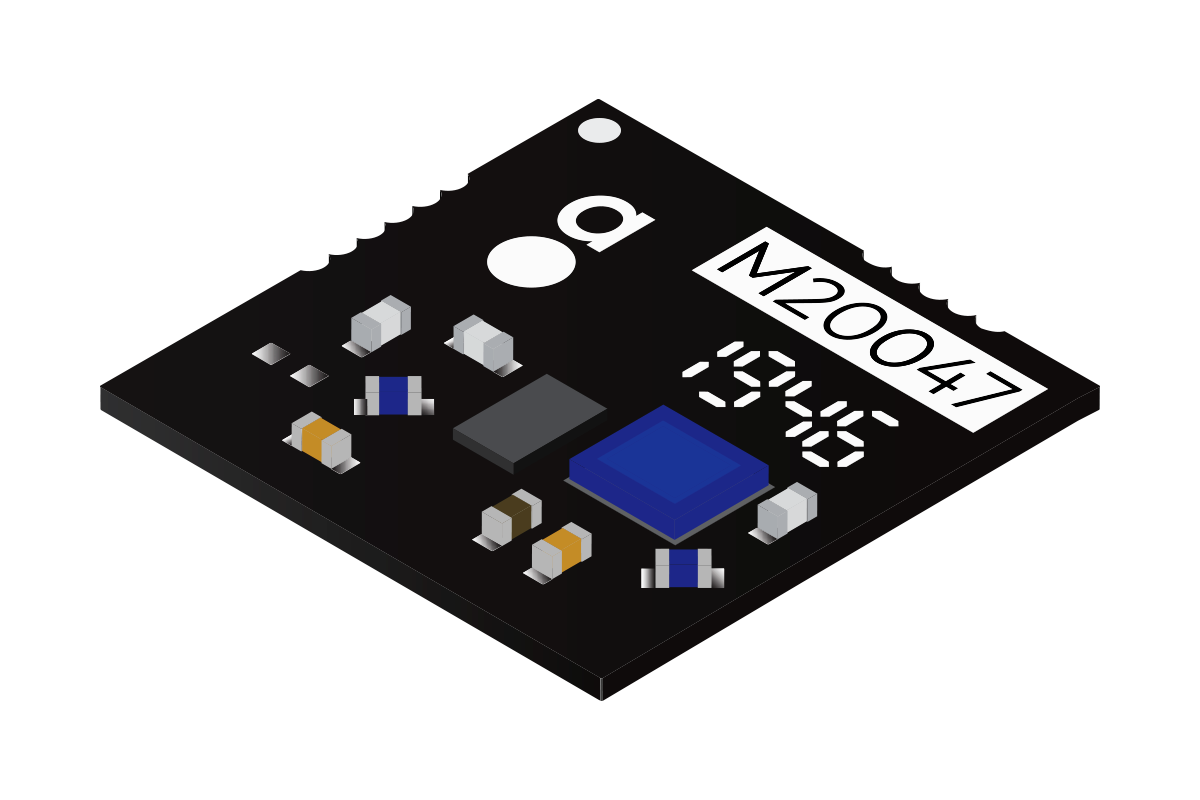
GNSS antenna module with filter and LNA
An active SMD GNSS antenna that is suitable for all global public constellations of GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and GALILEO. M20047-1 comes in an ultra-small SMD package at 7.0×7.0×0.9mm and has great performance and efficiency, making it perfect for applications such as portable devices and asset tracking.